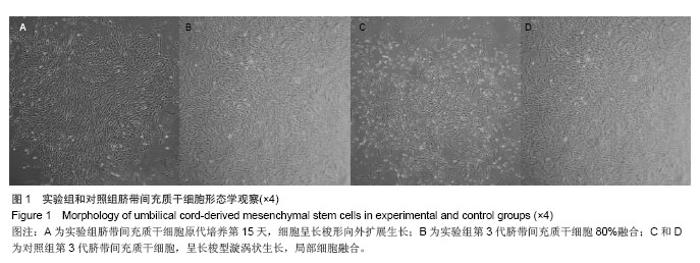
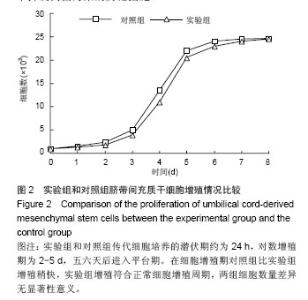
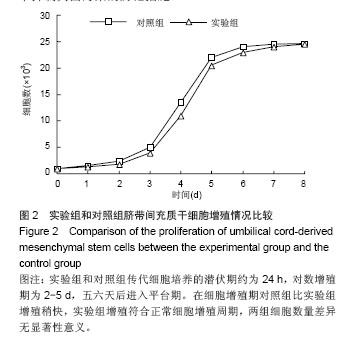
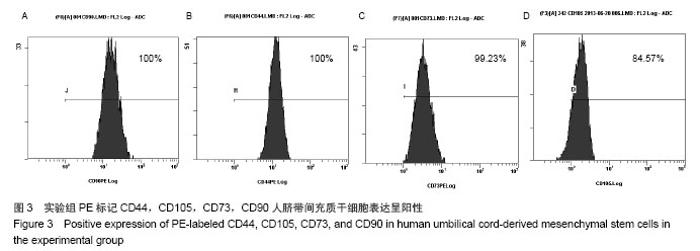
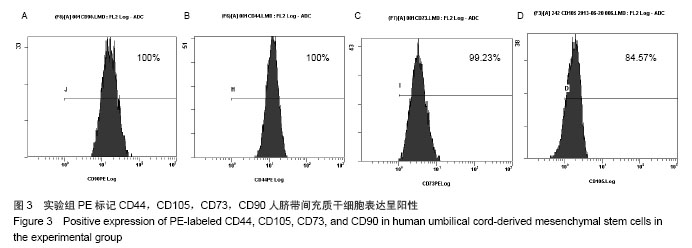
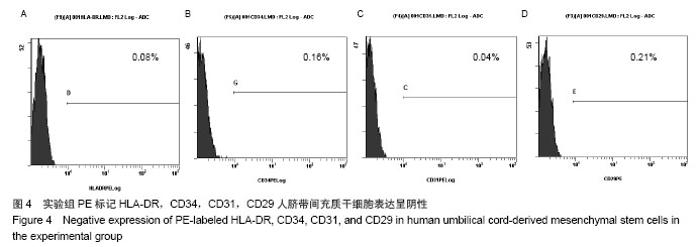
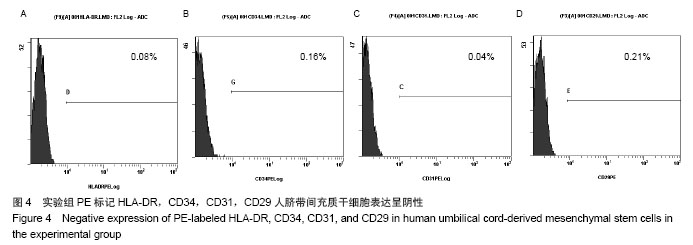
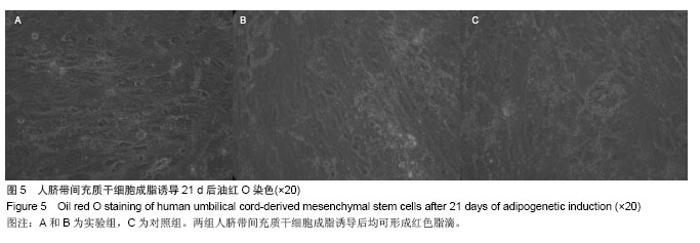
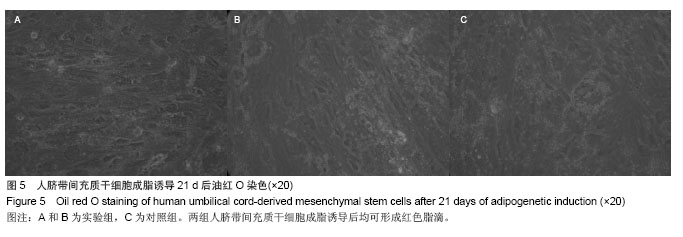
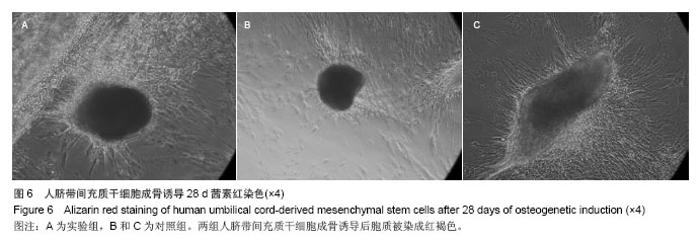
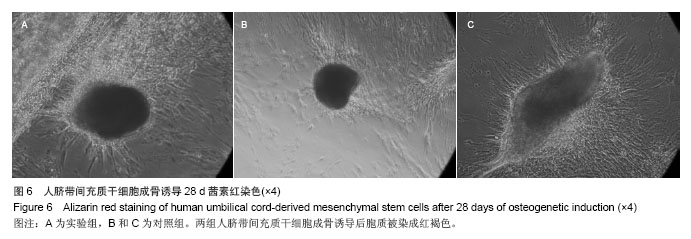
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (28): 4479-4484.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.28.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cultivation and differentiation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells treated with amphotericin B
Huang Wen-jing1, Liu Jun-jiang1, Zhou Jian-yu1, Hong Jing-xin 1, 2, Li Qian 1, 2, Han Jun-ling 1, 2
- 1 Union Stem Cell & Gene Engineering Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300384, China; 2 Hematopathy Hospital, Hematology Institute of Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin 300020, China
-
Online:2014-07-02Published:2014-07-02 -
Contact:Han Jun-ling, Researcher, Union Stem Cell & Gene Engineering Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300384, China; Hematopathy Hospital, Hematology Institute of Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin 300020, China -
About author:Huang Wen-jing, Studying for master’s degree, Technician-in-charge, Assistant researcher, Union Stem Cell & Gene Engineering Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300384, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Wen-jing, Liu Jun-jiang, Zhou Jian-yu, Hong Jing-xin, Li Qian, Han Jun-ling. Cultivation and differentiation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells treated with amphotericin B[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(28): 4479-4484.
share this article
| [1]Friedenstein AJ, Deriglasova UF, Kulagina NN,et al. Precursors for fibroblasts in different populations of hematopoietic cells as detected by the in vitro colony assay method.Exp Hematol. 1974;2(2):83-92.
[2]Deans RJ, Moseley AB.Mesenchymal stem cells: biology and potential clinical uses.Exp Hematol. 2000;28(8):875-884.
[3]Minguell JJ, Conget P, Erices A.Biology and clinical utilization of mesenchymal progenitor cells.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2000; 33(8):881-887.
[4]Quesenberry PJ, Abedi M, Aliotta J,et al.Stem cell plasticity: an overview.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2004;32(1):1-4.
[5]Nöth U, Osyczka AM, Tuli R,et al.Multilineage mesenchymal differentiation potential of human trabecular bone-derived cells.J Orthop Res. 2002;20(5):1060-1069.
[6]Rogers I, Casper RF.Umbilical cord blood stem cells.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2004;18(6):893-908.
[7]Zvaifler NJ, Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Adams G,et al. Mesenchymal precursor cells in the blood of normal individuals. Arthritis Res. 2000;2(6):477-488.
[8]Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B,et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells.Lancet. 2004;363 (9419):1439-1441.
[9]Kassem M, Abdallah BM.Human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: biological characteristics and potential role in therapy of degenerative diseases.Cell Tissue Res. 2008;331(1):157-163.
[10]Nakamizo A, Marini F, Amano T,et al.Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of gliomas.Cancer Res. 2005;65(8):3307-3318.
[11]张学锋,张美荣,胡剑霞,等.异种脐带间充质干细胞静脉应用的安全性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(32): 5971- 5975.
[12]Sobolewski K, Bańkowski E, Chyczewski L,et al.Collagen and glycosaminoglycans of Wharton's jelly.Biol Neonate. 1997; 71(1):11-21.
[13]Secco M, Zucconi E, Vieira NM,et al.Multipotent stem cells from umbilical cord: cord is richer than blood.Stem Cells. 2008; 26(1):146-150.
[14]Wexler SA, Donaldson C, Denning-Kendall P,et al.Adult bone marrow is a rich source of human mesenchymal 'stem' cells but umbilical cord and mobilized adult blood are not.Br J Haematol. 2003;121(2):368-374.
[15]Romanov YA, Svintsitskaya VA, Smirnov VN.Searching for alternative sources of postnatal human mesenchymal stem cells: candidate MSC-like cells from umbilical cord.Stem Cells. 2003;21(1):105-110.
[16]Seshareddy K, Troyer D, Weiss ML.Method to isolate mesenchymal-like cells from Wharton's Jelly of umbilical cord.Methods Cell Biol. 2008;86:101-119.
[17]Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton's jelly of the human umbilical cord.Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1330-1337.
[18]Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E,et al.Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):319-331.
[19]Sarugaser R, Lickorish D, Baksh D,et al.Human umbilical cord perivascular (HUCPV) cells: a source of mesenchymal progenitors.Stem Cells. 2005;23(2):220-229.
[20]Baksh D, Yao R, Tuan RS.Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow.Stem Cells. 2007;25(6):1384-1392.
[21]Chen MY, Lie PC, Li ZL,et al.Endothelial differentiation of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in comparison with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Exp Hematol. 2009;37(5):629-640.
[22]Mitchell KE, Weiss ML, Mitchell BM,et al.Matrix cells from Wharton's jelly form neurons and glia.Stem Cells. 2003; 21(1):50-60.
[23]杨军凤.妊娠期外阴阴道念珠菌感染患者的临床治疗[J].世界最新医学信息文摘:电子版,2012,12(6):100-101.
[24]任保艳,杨文勇.真菌性阴道炎患者菌种分布及耐药性分析[J].医学理论与实践,2011,24(1):67-68.
[25]赵林,申延清,荣春,等.间充质干细胞培养与分化诱导的特点及机制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(40):7551-7554.
[26]Stenderup K, Justesen J, Clausen C,et al.Aging is associated with decreased maximal life span and accelerated senescence of bone marrow stromal cells.Bone. 2003;33(6): 919-926.
[27]Mueller SM, Glowacki J.Age-related decline in the osteogenic potential of human bone marrow cells cultured in three-dimensional collagen sponges.J Cell Biochem. 2001; 82(4):583-590.
[28]祝加学,沈尊礼,秦金保,等.一种大量快速分离脐带间充质干细胞的新方法[J].现代生物医学进展,2010,10(6):1164-1169.
[29]Heino TJ, Hentunen TA.Differentiation of osteoblasts and osteocytes from mesenchymal stem cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2008;3(2):131-145.
[30]Ma L, Feng XY, Cui BL,et al.Human umbilical cord Wharton's Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into nerve-like cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2005;118(23):1987-1993.
[31]郭艳萍,李强,张爱君,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的培养及成骨诱导分化[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(3):683.
[32]陈妍,潘丽杰,袁杰,等.冻存脐带间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(36):6436-6442.
[33]洪敬欣,刘剑,李琳芳,等.地塞米松浓度与脐带间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4204-4211.
[34]汪涛,林晓波,杨丽娜,等.人脐带间充质干细胞向心肌细胞诱导分化并体内移植的研究[J].中国现代医生,2013,51(11):1-4.
[35]仇普斌,刘超,李伟,等.诱导人脐带间充质干细胞向心肌细胞分化及对小鼠心肌梗死的治疗作用[J].中国实验动物学报,2012, 20(5):9-14.
[36]阮中宝,杨向军,陈各才,等.体外培养和诱导人脐带源间充质干细胞定向分化为心肌细胞的实验研究[J].山东医药,2011,51(41): 64-65.
[37]王卫民,丁妍.BHA诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为神经细胞[J].东南大学学报:医学版, 2013,32(2):201-205.
[38]陈有,冯世庆,吴秋丽,等.人雪旺细胞促进人脐带间充质干细胞向神经方向分化的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(5): 930-932.
[39]王宪英,吴红海,秦亚斌,等.脑组织匀浆诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为神经样细胞[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(7):1439-1441.
[40]李振勇,李明,卢国辉,等.脐带间充质干细胞的分离培养及诱导分化为多巴胺能样神经元[J].中华神经医学杂志,2011,10(3): 241-245.
[41]毛希宏,杨智勇,孟明耀,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的培养鉴定及其向神经元细胞分化的研究[J].昆明医学院学报,2011,32(1): 41-47.
[42]禹亚彬,陈维,卞建民,等.体外定向诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛样细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(6):1012-1017.
[43]陈桃,王云帅,谷乐辉,等.胰岛新生相关蛋白肽在促进脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛素分泌细胞中的作用[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2013,29(2):141-145.
[44]李世龙,刘毅,惠玲,等.携带人胰岛素基因腺病毒载体转染人脐带间充质干细胞及其成脂分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(6): 999-1003. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [5] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [6] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [7] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [8] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [9] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [10] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [11] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [12] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [13] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [14] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||